In Bosnia and Herzegovina, the tax system is based on regulations that are adopted at different levels of decision-making and which together make up the tax system of our country. Tax regulations are enacted at the following levels:
- at the level of the state of Bosnia and Herzegovina;
- at the entity level - the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Republika Srpska;
- at the level of the Brčko District of Bosnia and Herzegovina;
- at the level of cantons within the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina;
- at the level of local self-governments in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Republika Srpska.
At the level of Bosnia and Herzegovina, only indirect taxes are collected, the collection of which is accumulated in a single account, and later distributed proportionally to the entities. In addition to the collection of value added tax (VAT), the Indirect Taxation Authority is also responsible for the collection of customs duties, tolls and excises. Indirect taxes are paid to the direct account of the Indirect Taxation Authority, with an indication of the code of local self-government, cantons and entities. On this basis, the percentages for the allocation of funds to the entities are determined later, and the entities further distribute them to the cantons and / or local governments.
All other taxes, fees, charges are collected and legally defined at the level of the entities of the Republika Srpska, the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and the Brčko District of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Furthermore, competencies within the entities are delegated to the level of cantons and to the level of local self-government in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, ie only to the level of local self-government in the Republika Srpska.
Note: For all tax and contribution calculations, we suggest hiring a certified accountant.
PROFIT TAX
A business entity registered in Bosnia and Herzegovina pays a tax on the realized profit in the amount of 10% in total, which makes Bosnia and Herzegovina extremely competitive with European countries, where the average profit tax rate is 30 %.
Profit is calculated at the beginning of the year (for each previous year) by deducting expenses from income, based on the completed tax return, which is submitted with the signature of a certified accountant no later than March 30. current year. The tax base includes profit, income and capital gains.
A taxpayer is an economic entity and another legal entity that performs economic activity independently and permanently by selling products and providing services on the market in order to make a profit. This means that the tax is paid by both residents and non-residents, if the profit is acquired in the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The taxpayer is a business entity and other legal entity that performs business independently and permanently by selling products and providing services on the market for profit. This means that the tax is paid by both residents and non-residents, if the profit is acquired on the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The Laws on Profit Tax of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republika Srpska define a resident as a legal entity whose registered office is registered in any of the 2 entity, where the actual administration and supervision of the business is located in one of the entities in the state. A non-resident is a legal entity that is established and whose headquarters are or whose actual management and supervision over operations outside the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and performs activities in Bosnia and Herzegovina through a business unit or occasionally. Non-resident - legal entity is taxed profit generated by performing activities through a business unit which is registered on the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina or which on other grounds are considered a business unit in accordance with the law.
Profits transferred from abroad are not taxed if they are previously subject to taxation abroad.
The period for which income tax is determined is a calendar year. However, this period may be shorter than a calendar year in the case of:
- Cessation of operations before the end of the calendar year;
- Start of business during the year;
- Status changes and the like.
The taxpayer is obliged to submit a correctly and accurately completed tax return with the tax balance to the competent branch office of the Tax Administration, as follows: For the tax period ending on 31.12. of the current or current year, the income tax return with tax balance and other attachments is submitted to the competent tax office within a maximum of 30 days after the deadline prescribed for submission of annual financial statements - ie by 30.03. For the tax period ending during the calendar year (cessation of business, status changes, etc.), the income tax return with tax balance and other attachments is submitted to the competent tax office within a maximum of 90 days from the last day of such tax period.
SALARY CONTRIBUTIONS
On the agreed net salary, the employer in Bosnia and Herzegovina also pays salary contributions. Unlike some European countries, in Bosnia and Herzegovina all wage-related contributions are made by the employer for the worker. In other words, although the contributions are divided into those borne by the employee and those borne by the employer, in practice the employer pays all contributions. A practical example of calculating the salary for a worker to whom the employer wants to pay the amount of 1.000,00 KM per month:
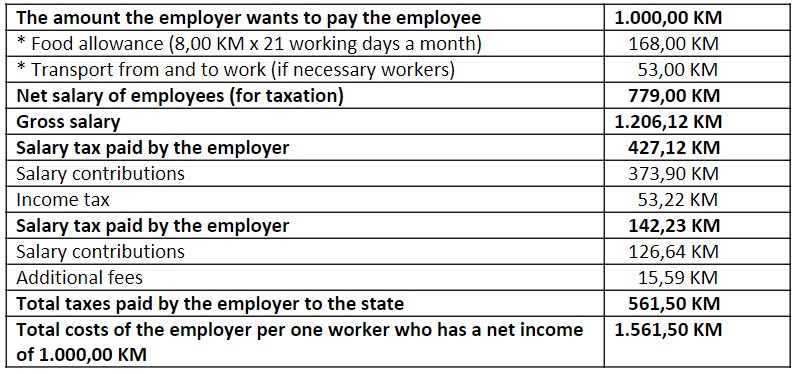
Income tax in Bosnia and Herzegovina (Federation Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republika Srpska) is 10 % and is paid by the employer, together with contributions, by transferring funds through the bank from the regular account for performing the registered activity.
The income tax calculation system works as follows:
Each natural person has a personal deduction of 300.00 KM based on a coefficient of 1.0, which reduces the amount for taxation. If you have family members that you support or you have benefits on other grounds, the coefficient can be higher, which increases your personal deduction, and thus a lower income tax will be calculated. On the example of a net salary of 1,000.00 KM, the calculated income tax is 77.00 KM.
PROPERTY TAX
One of the tax areas in Bosnia and Herzegovina that is not uniform in the country is the issue of real estate tax. The property tax is not uniform at the state level, but is regulated by regulations at the level of cantons in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and at the level of the Republika Srpska.
Given that the focus of this platform is on the Zenica-Doboj Canton, here we will present the property tax only in the entity of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Property taxation is not regulated at the entity level in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, but is regulated by laws in each of the 10 cantons. According to cantonal laws, property, cottages, business premises, rented apartments, garages, motor vehicles, aircraft and vessels are taxed. Property tax is paid annually per square meter.
The cantons are independent in determining the amount of tax, so there is a different practice of distributing these revenues. Some cantons share revenue with local governments, while in other cantons all revenue is distributed to local governments.
More information on regulations at the cantonal levels can be found on the page of the Tax Administration of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
In the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, citizens do not pay taxes for their own housing, ie for apartments and houses, while cottages - holiday homes are taxed.
The Law on Income Tax in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina on income from property rights, such as rent, lease, etc., pays a tax of 10 % per annum.
COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGES OF BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA
Bosnia and Herzegovina is the country with the lowest rates in the region and in Europe, according to the following tax rates: Bosnia and Herzegovina is the country with the lowest rates in the region and in Europe, according to the following tax rates:
- Value added tax (VAT) = 17 %;
- Income tax = 10 %;
- Income tax = 10 %;
- Tax on dividend withdrawal = 0 %.
Bosnia and Herzegovina has a single income tax rate of 10 %, with additional benefits for workers. In the countries of the region, progressive taxation of income with tax rates is carried out. Thus, in the Republic of Croatia taxes amount to 12.25 % and 40 %, and in the Republic of Serbia 10.15 % and 20 %. In the Republic of Slovenia they range from 16 % to 41 %, and in EU countries income tax rates range from 15 % to 51 %, without contributions.
These are the comparative advantages of Bosnia and Herzegovina for investors when considering investment projects in our country. These tax rates make Bosnia and Herzegovina extremely competitive compared to the rest of Europe, where the average corporate tax rate is 30 %.
